Different Proxy Servers

Types of Proxy Servers – eduCBA
Introduction to Proxy Servers
Proxy Servers are referred to those servers that act as an intermediary to the request made by clients to a particular server for some services or request for some resources. Several types of proxy servers are available whose use will depend on the purpose of a request made by the clients to the servers. The purpose of Proxy servers is to Protects the direct connect of Internet clients and internet and internet resources: Proxy server prevents the identification of the client’s IP address while any request is made to any other servers.
Internet clients and internal resources: Proxy servers also act as a shield for an internal network against the request coming from a client to access the data on that server. The original IP address of the node remains hidden while accessing data from that server.
Protects true host identity: Outgoing traffic appears to come from the proxy server. It must be configured to the specific application, e. g. HTTPS or FTP.
For example, as a client to MNC, a client can use a proxy to observe its contract employees’ traffic to get the work efficiently done. It can also be used to keep a check on any leakage of internal highly confidential data. Some can also use it to increase their websites rank and get the traffic diverted anonymously.
The need for Private Proxy
Some of the need for a private proxy is mentioned below:
Defeat Hackers
Every organization has its own personal data that need to protect from malicious use. Thus, passwords are used, and different architects are set up, but there is still a possibility that this information can be hacked if the IP address is accessible easily. Proxy servers are set up to prevent tracking of the original IP address; instead, data is shown to come from a different IP address.
Filtering of the Content
Proxy servers also help filter out the content that doesn’t follow the web application’s policies or server required. It provides a facility to authenticate the user and provides the logs of URL of users requests made through that proxies.
Content can be Cached.
The proxy also helps in caching the content of the websites. This helps in fast access to the data that has been accessed oftenly.
Examine Packet Headers and Payloads
We can also examine the payloads and packet headers of the nodes in the internal server’s requests so that any access to social websites can be easily tracked and restricted.
Types of Proxy Servers
Below are the different types of proxy servers:
1. Reverse Proxy
This represents the server. In case there are multiple websites on different servers, then it is the job of a reverse proxy server to listen to the client’s request and redirect to the particular web server.
Example – Listen for TCP port 80 website connections. These are normally placed in a DMZ zone for publicly accessible services and protect the host’s true identity. It is transparent to the external users as external users will not be able to identify the actual number of internal servers. It is the duty of reverse proxy to redirect the flow depending on the configurations of internal servers. The request made to pass through the private network protected by firewalls needs a proxy server that does not abide by any local policies. This type of request from the clients are completed using reverse proxy servers. This is also used to restrict the client’s access to the sensitive data residing on the particular servers.
2. Web Proxy Server
This type of proxies forward the HTTP requests. This request is the same as HTTP requests; only URL is passed instead of a path. A request is sent to which the proxy server responds. Examples of such proxies are Apache, HAPProxy.
The client-server Proxy auto-config protocol solves the solution to the problems of multiple proxy servers.
3. Anonymous Proxy
This is the type of proxy server that does not makes an original IP address. Although these servers are detectable still provides rational anonymity to the client device.
4. High Anonymity Proxy
This proxy server does not allow the original IP address to be detected, and no one can detect it as a proxy server.
5. Transparent Proxy
This type of proxy server never provides any anonymity to the client; instead, an original IP address can be easily detected using this proxy. Still, it is being used to act as a cache for the websites.
A transparent proxy combined with gateway results in a proxy server where the client IP’s connection requests are redirected. This redirection occurs without the client IP address configuration. This redirection can be easily detected by the HTTP headers present on the server-side.
These are also known as intercepting proxies, inline proxy, and forged proxy.
Working: It intercepts the communication at the network level without the need for any configuration. It also works as a gateway or router that authenticates the communication without making any changes to the requests or responses passing through the server.
Uses: These types of proxies are most commonly used at the business level to enforce the policy over communication. It also tries to prevent any attack on TCP servers example – denial-of-service attack.
6. CGI Proxy
This type of proxies was developed to make the websites more accessible.
Working: It accepts the requests to target URLs using a web form, processes it and returns the result to the web browser. It is less popular due to VPNs and other privacy policies, but it still receives many requests these days. Its usage reduces because of excessive traffic that can be caused to the website after passing the local filtration, leading to collateral damage to the organization.
7. Suffix Proxy
This type of proxy server appends the proxy’s name to the URL to the content that has been requested to the proxy. This type of proxy doesn’t preserve a higher level of anonymity.
Uses: It is used for bypassing the web filters. This proxy is easy to use and can be easily implemented but is used less due to more or more web filters.
8. Distorting Proxy
Proxy servers can generate an incorrect original IP address of clients once being detected as a proxy server. It uses HTTP headers to maintain the confidentiality of the Client IP address.
9. TOR Onion Proxy
It is software that aims at online anonymity to the user’s personal information.
Working: It routes the traffic through various networks present worldwide to make it difficult to track the users’ address and prevent the attack of any anonymous activities. It makes it difficult for any person who is performing traffic analysis to track the original address. For this, it uses ONION ROUTING.
In this type of routing, the information is encrypted in a multi-folds layer by layer to prevent it. At the destination, each layer is decrypted to prevent the information from scrambling or getting distorted.
This software is open source as well as free of cost to use.
10. I2P Anonymous Proxy
It is an anonymous network enhanced version of the Tor onion proxy, which uses encryption to hide all the communications at various levels. This encrypted data is then relayed through various network routers present in different locations. Thus I2P is a fully distributed proxy that aims at online anonymity. It also implements garlic routing. (enhanced version of Tor’s pnion routing. It provides a proxy to all protocols. This type of proxies can be run on the node.
I2P router finds other peers to build an anonymous identity to protect the user’s personal information.
This software and network are free of cost and open source to use; It also resists censorship.
11. DNS Proxy
Unlike other proxies, this type of proxy takes requests in the form of DNS queries and forward them to the Domain server, where they can also be cached, and the flow of requests can also be redirected.
Types of Proxy Servers (Protocols)
Below are the different types of proxy servers protocols:
Socks Proxy Server: This type of proxy server provides a connection to a particular server. Depending on Socks protocols, this type of server allows the multilayering of various data types such as TCS or UDP.
FTP Proxy Server: This type of proxy server caches FTP requests’ traffic and uses the concept of relaying.
HTTP Proxy Server: This proxy was developed to process a one-way request to the web pages using HTTP protocols.
SSL Proxy Server: This type of server was developed using the concept of TCP relaying being used in the SOCKS proxy protocol to allow Web Pages’ requests.
Conclusion
Proxy servers help in various anonymity types required at different levels, either as a client or as a service provider. It helps to resist the security of information of various users as well as the internal network. Different types of proxies are available, which follow various routing protocols and serve different uses at different anonymity levels.
Proxifiers are the client programs that allow the adaptation of any type of software used for networking using various types of proxy servers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Proxy Servers. Here we discuss the basic concept, need, types and various protocols of Proxy Servers in detail. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
TCP/IP Model
SOAP vs HTTP
What is TCP/IP?
Linux Proxy Server
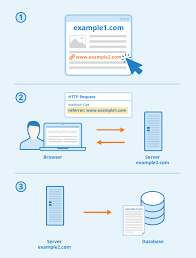
Proxy vs. VPN: 4 differences you should know – Norton
Worried about your privacy when searching the Internet? Wondering if hackers, government agencies, or companies can track what sites you visit, files you download, or links you click?
You might be wondering if it’s time to sign up with a virtual private network (VPN) or proxy server to hide your location and internet-service-provider address from any snoops.
But be aware: There are significant differences between a proxy and a VPN. While both tools can protect your identity, only a VPN will encrypt your data as you browse the web.
This means that only a VPN can help hide your online activity from hackers, government agencies, and companies that might be looking to learn more about how you spend your time on the internet.
What VPNs and proxy servers are
Both VPNs and proxy servers are tools you can use to help keep your activity private when browsing the internet, sending emails, reading online message boards, streaming video, and downloading files. But both of these tools work in different ways.
A proxy server is a computer that sits between you and a server, acting as a gateway when you access the internet. When you connect to a specific website, video-streaming app, or file-sharing program from your laptop, tablet, smart phone, or any other device, you can first connect to a proxy. Once you do this, you’ll be connecting to the site or app through an outside host server.
There’s a clear benefit to this if you want to hide your identity. The website you are visiting — or the streaming service you are accessing or file-sharing site you are using — will only see the IP address belonging to the proxy server. It won’t see your address. This will keep your identity and true location hidden from these sites and apps.
There are different types of proxies. Here are three of the most common ones.
HTTP proxies
You’d use these proxies to access websites. You can also use this type of proxy to access geo-restricted content. For instance, maybe an online video is restricted in your region. You can use a proxy server to log onto the site hosting the video, hiding the fact that your original IP address is restricted from watching it. Keep in mind, this may violate the user agreement with your content provider.
SOCKS5 proxies
These proxies don’t work only on websites. You can use a SOCKS5 proxy to access video streaming services, file-sharing sites, or online games. Be aware, though, that connecting to an app through a SOCKS5 proxy might be slower because free proxies can have less configuration options, support, and slower infrastructure.
Transparent proxies
You might have used a transparent proxy without realizing that. That’s the whole point. Employers — or parents, schools or libraries — might set up a transparent proxy as a way to filter user’s content when they connect to the internet or block users from accessing certain websites.
A VPN is similar to a proxy, but instead of working with single apps or websites, it works with every site you visit or app you access.
Like a proxy, when you visit a website after first logging into a VPN, your IP address is hidden and replaced with the IP address of your VPN provider. This keeps your identity shielded. But unlike a proxy, this protection will remain in place as you surf to new websites, visit online streaming sites, or send emails or download files.
You can access the internet through free VPN providers. But providers that charge for VPN access are less likely to share data with third parties.
How VPNs and proxies differ
Here are four ways VPNs and proxies are different.
1. VPNs encrypt your information
The biggest benefit of a VPN over a proxy server? With VPN enabled, your browsing and any data you send or receive, will be encrypted. This is important: It means that hackers, government agencies, businesses, or anyone else won’t be able to see what you’re doing when online.
Say you access your online bank account while using a VPN. Because your information is encrypted, hackers won’t be able to access your bank account numbers. The same is true if you log onto your credit card provider’s online portal: Because your data is encrypted, criminals won’t be able to snag your credit card number or the password you use to log onto the portal.
2. VPN providers promote online privacy
If you want total privacy, work with a VPN provider that has a no-log policy. “No log” means the providers pledge not to track and store your activity while you are using the service to connect to the internet. This means that these providers won’t have any data to give to anyone else who wants information about what sites you browse or files you share. On the other hand, a free proxy may monitor traffic and sell data to third-parties.
3. Free proxy connections can be slower
Both proxy servers and VPNs can slow down your browsing, depending on how many users are accessing these services. Free proxy connections however can be slower and less secure because of less support, less configuration options, and slower infrastructure.
4. You may spend more with a VPN
You can connect through free VPNs. However, many tech experts recommend going with a VPN provider that charges a fee because paid services often offer more data privacy, more secure connections, and more reliable performance. Security of free VPN can be unreliable, as many providers use only one VPN connection, called point-to-point tunneling protocol (PTTP). A paid VPN service, on the other hand, can offer users data encryption which is more secure.
Do you need a proxy if you have a VPN?
No. A VPN and proxy server both mask your IP address. But a VPN will also encrypt the data you send and receive, something that a proxy server doesn’t do. If you are already using a VPN, then, connecting to a website or app through a proxy server would be an unnecessary step.
What should you use, a VPN or proxy server?
When it comes to proxy vs. VPN and which one to use, the differences between the two might help you decide what’s the best choice for you.
If you want to hide your IP address, using either a proxy server or VPN will work. And if you’re worried about browsing speed, and you’re only worried about hiding your IP address from a single site or app, then a free proxy server will do the job.
If cost is an issue, then connecting to single sites, apps, or file-sharing services through a proxy server might be the smart move. It’s easy to find free proxy servers that will hide your IP address.
But if you want to keep your browsing activity hidden from snoops, logging onto the internet through a VPN is the better choice. Again, it comes down to encryption: VPNs encrypt your data while online. Proxy servers don’t.
If you plan to access several sites while online, especially if you’re connecting to sites such as your bank account or credit card portal, a VPN provides more security.
And while many of the preferred VPN providers will charge for their services, this price might be a small one to pay if it means that your most sensitive personal and financial information is shielded from the eyes of online snoops.

About proxy servers – Indiana University Knowledge Base
A proxy server, also known as a “proxy” or “application-level gateway”, is a computer that acts as a gateway between a local network (for example, all the computers at one company or in one building) and a larger-scale network such as the internet. Proxy servers provide increased performance and security. In some cases, they monitor employees’ use of outside resources.
A proxy server works by intercepting connections between sender and receiver. All incoming data enters through one port and is forwarded to the rest of the network via another port. By blocking direct access between two networks, proxy servers make it much more difficult for hackers to get internal addresses and details of a private network.
Some proxy servers are a group of applications or servers that block common internet services. For example, an HTTP proxy intercepts web access, and an SMTP proxy intercepts email. A proxy server uses a network addressing scheme to present one organization-wide IP address to the internet. The server funnels all user requests to the internet and returns responses to the appropriate users. In addition to restricting access from outside, this mechanism can prevent inside users from reaching specific internet resources (for example, certain websites). A proxy server can also be one of the components of a firewall.
Proxies may also cache web pages. Each time an internal user requests a URL from outside, a temporary copy is stored locally. The next time an internal user requests the same URL, the proxy can serve the local copy instead of retrieving the original across the network, improving performance.
Note:
Do not confuse a proxy server with a
NAT (Network Address Translation) device. A proxy server connects to, responds to, and receives traffic from the internet, acting on behalf of the client computer, while a NAT device transparently changes the origination address of traffic coming through it before passing it to the internet.
For those who understand the OSI (Open System Interconnection) model of networking, the technical difference between a proxy and a NAT is that the proxy server works on the transport layer (layer 4) or higher of the OSI model, whereas a NAT works on the network layer (layer 3).
This is document ahoo in the Knowledge Base.
Last modified on 2018-11-15 11:25:00.
Frequently Asked Questions about different proxy servers
What is the best type of proxy server?
Residential proxies are by-far the best proxies for most uses, because they are IP addresses of real, physical devices. They appear as average users to all servers, and are almost impossible to detect (unless the proxy user abuses it). Using a residential proxy makes gaining access to data easy.
Is a VPN a proxy server?
A VPN is similar to a proxy, but instead of working with single apps or websites, it works with every site you visit or app you access. Like a proxy, when you visit a website after first logging into a VPN, your IP address is hidden and replaced with the IP address of your VPN provider.
What is the most common proxy server?
A forward proxy is the most common form of a proxy server and is generally used to pass requests from an isolated, private network to the Internet through a firewall.