What Are Cookies Used For
How Google uses cookies – Privacy & Terms
A cookie is a small piece of text sent to your browser by a website you visit. It helps the site remember information about your visit, which can make it easier to visit the site again and make the site more useful to example, we use cookies to remember your preferred language, to make the ads you see more relevant to you, to count how many visitors we receive to a page, to help you sign up for our services, to protect your data, and to remember your ad page describes the types of cookies used by Google. It also explains how Google and our partners use cookies in advertising. See the Privacy Policy to learn how we protect your privacy in our use of cookies and other or all of the cookies described below may be stored in your browser. To manage how cookies are used, you can refuse the use of certain cookies through your Google personalization settings anytime by visiting You can also manage cookies in your browser (though browsers for mobile devices may not offer this visibility). For example, if you use Google Chrome as your browser, you can visit chromesettings/ctionalityCookies used for functionality allow users to interact with a service or site to access features that are fundamental to that service. Things considered fundamental to the service include preferences like the user’s choice of language, product optimizations that help maintain and improve a service, and maintaining information relating to a user’s session, such as the content of a shopping cookies are used to maintain a user’s preferences. For example, most people who use Google services have a cookie called ‘NID’ in their browsers. This cookie contains a unique ID used to remember your preferences and other information such as your preferred language, how many search results you prefer to have shown on a results page (for example, 10 or 20), and whether you want to have Google’s SafeSearch filter turned on. Each NID cookie expires 6 months from a user’s last use. A cookie called ‘VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE’ serves a similar purpose for YouTube and is also used to detect and resolve problems with the Tube uses the ‘PREF’ cookie to store information such as a user’s preferred page configuration and playback preferences like autoplay, shuffle content, and player size. For YouTube Music, these preferences include volume, repeat mode, and autoplay. This cookie expires 8 months from a user’s last cookies are used to maintain and enhance a user’s experience during a specific browsing session. For example ‘YSC’ is used by YouTube to remember user input and associate a user’s actions. This cookie lasts for as long as the user keeps their browser open. The cookie ‘pm_sess’ also helps maintain a user’s browser session and lasts for 30 cookies improve the performance of Google services. For example, ‘CGIC’ improves the delivery of search results by autocompleting search queries based on a user’s initial input. This cookie lasts for 6 curityCookies used for security authenticate users, prevent fraud, and protect users as they interact with a cookies are used to authenticate users, helping ensure that only the actual owner of an account can access that account. For example, cookies called ‘SID’ and ‘HSID’ contain digitally signed and encrypted records of a user’s Google Account ID and most recent sign-in time. The combination of these cookies allows us to block many types of attack, such as attempts to steal the content of forms submitted in Google cookies are used to prevent spam, fraud, and abuse. For example, the ‘pm_sess’ and ‘YSC’ cookies ensure that requests within a browsing session are made by the user and not by other sites. Both cookies prevent malicious sites acting without a user’s knowledge and as if they were that Cookies used for analytics help collect data that allows services to understand how users interact with a particular service. These insights allow services both to improve content and to build better features that improve the user’s cookies help sites understand how their visitors engage with their properties. For example, Google Analytics, a Google product that helps site and app owners understand how people engage with a service, uses a set of cookies to collect information and report site usage statistics without personally identifying individual visitors to Google. ‘_ga’ is the main cookie used by Google Analytics. ‘_ga’ enables a service to distinguish one user from another and lasts for 2 years. It’s used by any site that implements Google Analytics, including Google services also use analytics cookies like these, as well as others like ‘NID’ on Google Search and ‘VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE’ on vertisingGoogle uses cookies for advertising, including serving and rendering ads, personalizing ads (depending on your ad settings at), limiting the number of times an ad is shown to a user, muting ads you have chosen to stop seeing, and measuring the effectiveness of ads. ‘NID’ is used for these purposes to show Google ads in Google services for signed-out users‘IDE’ and ‘ANID’ are used for these purposes to show Google ads on non-Google sitesOther Google services like YouTube may also use these cookies and cookies like ‘VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE’ to show more relevant you have personalized ads enabled, ‘ANID’ is used to remember this setting and lasts for 13 months in the European Economic Area (EEA), Switzerland, and the United Kingdom (UK), and 24 months everywhere else. If you have disabled personalized ads, ‘ANID’ is used to store that setting until 2030. ‘NID’ expires 6 months from a user’s last use. ‘IDE’ lasts for 13 months in the EEA, Switzerland, and the UK and 24 months everywhere cookies used for advertising are for users who sign in to use Google services. For example, ‘DSID’ is used to identify a signed-in user on non-Google sites and to remember whether the user has agreed to ad personalization. It lasts for 2 rough Google’s advertising platform, businesses can advertise in Google services as well as on non-Google sites that partner with cookies support Google showing ads on third-party sites, and are set in the domain of the website you visit. For example, ‘_gads’ enables sites to show Google ads, including personalized ads. Cookies that start with ‘_gac_’ come from Google Analytics and are used by advertisers to measure user activity and the performance of their ad campaigns. The ‘_gads’ cookie lasts for 13 months and the ‘_gac_’ cookies last for 90 cookies are used to measure ad and campaign performance and conversion rates for Google ads on a site you visit. For example, cookies that start with ‘_gcl_’ come from Google Analytics and are primarily used to help advertisers determine how many times users who click on their ads end up taking an action on their site, such as making a purchase. Cookies used for measuring conversion rates aren’t used to personalize ads. ‘_gcl_’ cookies last for 90 rsonalizationCookies used for personalization enhance the user’s experience by providing personalized content and pending on your settings at, some cookies enable better recommendations within a service. For example, ‘VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE’ enables personalized recommendations on YouTube based on past views and searches. And ‘NID’ enables personalized autocomplete features in Search as users type search terms. These cookies expire 6 months after a user’s last use.

What Is The Purpose of a Cookie? – Knowledge Base – CookiePro
Cookies are used to carry information from website to website, or between sessions on related websites, without having to burden a server machine with massive amounts of data storage. If there is a large amount of information to store, then a cookie can simply be used as a means to identify a given user so that further related information can be looked up on a server-side database.
For example, the first time a user visits a site, they may choose a username which is stored in the cookie, and then provide data such as password, name, address, preferred font size, page layout, etc. This information would all be stored on the database using the username as a key. Subsequently when the site is revisited the server will read the cookie to find the username, and then retrieve all the user’s information from the database without it having to be re-entered.
Scan your website for free and take steps to comply with all the major global regulations with CookiePro!

Should you delete cookies? 6 reasons you probably should clear cookies
Security Center
Privacy
Should you delete cookies? 6 reasons you probably should clear cookies
May 25, 2021
When you surf the web, you’ve likely clicked on those pop-up requests that ask if you will accept cookies. The question becomes: If you’ve already accepted some cookies, should you delete them?
While this opt-in may seem harmless in its ease and simplicity, it’s important to understand what storing cookies could mean for your personal information and privacy.
What are computer cookies? They’re small packets of data saved as text files on the web browser of your computer or other devices. The website you’re visiting creates these cookies, or small bits of code, to collect data from your browsing history.
Cookies can be useful as they keep track of items in your shopping carts and save your personal information — including login credentials — so sites can remember you and your preferences. However, cookies also may undermine your privacy and security.
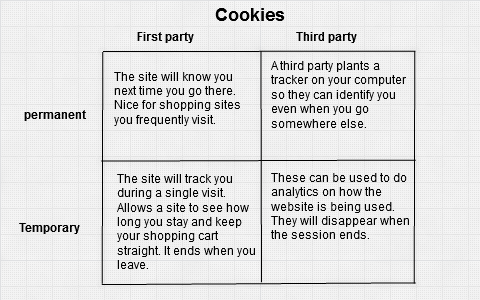
Deciding whether to accept or clear these cookies may depend on the kinds of cookies in question. Generally, there are three types of computer cookies.
Session cookies – text files that are stored in a temporary folder. Session cookies do not collect your personal data and are deleted when your browsing session ends.
Stored cookies – cookies that do track your online preferences, like login credentials, in order to improve your website experience. Stored cookies will expire after some time has passed.
Third-party cookies – the cookies that track you. Third-party cookies collect your data when you visit a website and may be shared with or sold to third-party advertisers.
Depending on which cookies you’re dealing with, they can pose a privacy risk due to the type of personal information they’re collecting — and what they’re doing with that data.
In this article, we discuss reasons why you may or may not want to delete cookies from your browser, along with how to clear tracking cookies from your browser.
Should You Delete Cookies?
Is having cookies a bad thing, or should you clear them? The answer depends on the website you’re visiting in terms of who will gain access to your data and what they will do with it, along with whether clearing cookies will affect your ability to use that site. Also, not all cookies are the same, as we highlight above.
There are several reasons why you may or may not want to delete cookies.
6 reasons you should delete cookies from your browser –
Here are six reasons why it may be a good idea to clear cookies from your browser.
An unencrypted website. If a website isn’t encrypted, then it isn’t protecting your privacy when it comes to computer cookies and your personal information. You’ll want to decline or delete them, if you’ve already opted in.
Third-party cookies. Third-party cookies can leave you vulnerable and should be declined or deleted if they’re already stored on your browser. Otherwise, a website owner could sell your browsing data to third parties like advertisers. The problem with third-party cookies is you would have no control over what the third parties do with your data. They – or someone they share the data with – could use your personal data to do things such as commit online crimes like identity theft.
Slower computer speeds. Although small, cookies do occupy space on your computer. If there are enough of them stored over a long period of time, they could slow down the speed of your computer and other devices.
Flagged, suspicious cookies. If your antivirus software flags suspicious cookies, you should delete them.
When using PII. Cookies can record your personally identifiable information — also known as PII or simply personal information — to do things like auto-fill forms on browsers. This information may include your name, address, account login credentials, and other personal data that could be used for nefarious purposes like identity theft and other online frauds. For example, say you’re planning on accessing your bank account information while online. You definitely should not accept cookies – and delete them if you mistakenly do.
Outdated cookies. If a website page has been updated, the cached data in cookies might conflict with the new site. This could give you trouble the next time you try to upload that page.
3 reasons you may not want to delete cookies from your browser
There also are reasons for why it may not be useful, or perhaps is inconvenient, to delete cookies from your browser.
Website access. One problem with refusing to accept cookies is that if you don’t accept cookies, some website owners may not allow you to use their websites.
A better user experience. In a similar way, you may not receive the full user experience on certain websites if you decline computer cookies. For example, cookies can remember and save helpful data about you, like your interests or leftover shopping cart items.
Easier, quicker log-ins. Computer cookies saved on your web browser can help you use your favorite websites more efficiently. They can make online transactions extremely convenient, as you don’t have to enter in your information every time you visit a site. Instead, logging into your favorite websites is quick and easy.
How to delete cookies from your browser
If cookies already are saved on your browser, there are ways to delete cookies from browsers. This article provides step-by-step instructions on how to clear cookies from the latest versions of Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and other popular web browsers.
As a general rule, you’ll go to your respective “Settings” and “Privacy” tabs, and then clear the cookies in your website browsing data and history. In addition to clearing your cache, you can customize which cookies will be deleted based on a specific time range and other options.
Taking into consideration what types of cookies are involved can help you decide if clearing these files is necessary to keep your personal information private and safe. Otherwise, if your sensitive data falls into the wrong hands, you may be leaving yourself vulnerable to online frauds like identity theft.
Cyber threats have evolved, and so have we.
Norton 360™ with LifeLock™, all-in-one, comprehensive protection against viruses, malware, identity theft, online tracking and much, much more.
Try Norton 360 with Lifelock.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. NortonLifeLock offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about cyber safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses.
Copyright © 2021 NortonLifeLock Inc. All rights reserved. NortonLifeLock, the NortonLifeLock Logo, the Checkmark Logo, Norton, LifeLock, and the LockMan Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of NortonLifeLock Inc. or its affiliates in the United States and other countries. Firefox is a trademark of Mozilla Foundation. Android, Google Chrome, Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google, LLC. Mac, iPhone, iPad, Apple and the Apple logo are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U. S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc. Alexa and all related logos are trademarks of, Inc. or its affiliates. Microsoft and the Window logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U. The Android robot is reproduced or modified from work created and shared by Google and used according to terms described in the Creative Commons 3. 0 Attribution License. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Frequently Asked Questions about what are cookies used for
What is the purpose of cookies?
Cookies are used to carry information from website to website, or between sessions on related websites, without having to burden a server machine with massive amounts of data storage.Apr 27, 2020
Should I delete cookies?
Although small, cookies do occupy space on your computer. If there are enough of them stored over a long period of time, they could slow down the speed of your computer and other devices. Flagged, suspicious cookies. If your antivirus software flags suspicious cookies, you should delete them.May 25, 2021
Are cookies on a website bad?
Are cookies bad? Cookies are not harmful; they don’t carry viruses or malware, and they don’t store personal information about you. But some websites may not be secure, which can allow hackers to intercept cookies and abuse the information they carry.Feb 26, 2020