Why Captcha Code Is Used
What Does CAPTCHA Mean? | CAPTCHA Types & Examples
What is CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA stands for the Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. CAPTCHAs are tools you can use to differentiate between real users and automated users, such as bots. CAPTCHAs provide challenges that are difficult for computers to perform but relatively easy for humans. For example, identifying stretched letters or numbers, or clicking in a specific area.
What are CAPTCHAs Used for
CAPTCHAs are used by any website that wishes to restrict usage by bots. Specific uses include:
Maintaining poll accuracy—CAPTCHAs can prevent poll skewing by ensuring that each vote is entered by a human. Although this does not limit the overall number of votes that can be made, it makes the time required for each vote longer, discouraging multiple votes.
Limiting registration for services—services can use CAPTCHAs to prevent bots from spamming registration systems to create fake accounts. Restricting account creation prevents waste of a service’s resources and reduces opportunities for fraud.
Preventing ticket inflation—ticketing systems can use CAPTCHA to limit scalpers from purchasing large numbers of tickets for resale. It can also be used to prevent false registrations to free events.
Preventing false comments—CAPTCHAs can prevent bots from spamming message boards, contact forms, or review sites. The extra step required by a CAPTCHA can also play a role in reducing online harassment through inconvenience.
How Does CAPTCHA Work
CAPTCHAs work by providing information to a user for interpretation. Traditional CAPTCHAs provided distorted or overlapping letters and numbers that a user then has to submit via a form field. The distortion of the letters made it difficult for bots to interpret the text and prevented access until the characters were verified.
This CAPTCHA type relies on a human’s ability to generalize and recognize novel patterns based on variable past experience. In contrast, bots can often only follow set patterns or input randomized characters. This limitation makes it unlikely that bots will correctly guess the right combination.
Since CAPTCHA was introduced, bots that use machine learning have been developed. These bots are better able to identify traditional CAPTCHAs with algorithms trained in pattern recognition. Due to this development, newer CAPTCHA methods are based on more complex tests. For example, reCAPTCHA requires clicking in a specific area and waiting until a timer runs out.
Drawbacks of Using CAPTCHA
The overwhelming benefit of CAPTCHA is that it is highly effective against all but the most sophisticated bad bots. However, CAPTCHA mechanisms can negatively affect the user experience on your website:
Disruptive and frustrating for users
May be difficult to understand or use for some audiences
Some CAPTCHA types do not support all browsers
Some CAPTCHA types are not accessible to users who view a website using screen readers or assistive devices
CAPTCHA Types: Examples
Modern CAPTCHAs fall into three main categories—text-based, image-based, and audio.
Text-based CAPTCHAs
Text-based CAPTCHAs are the original way in which humans were verified. These CAPTCHAs can use known words or phrases, or random combinations of digits and letters. Some text-based CAPTCHAs also include variations in capitalization.
The CAPTCHA presents these characters in a way that is alienated and requires interpretation. Alienation can involve scaling, rotation, distorting characters. It can also involve overlapping characters with graphic elements such as color, background noise, lines, arcs, or dots. This alienation provides protection against bots with insufficient text recognition algorithms but can also be difficult for humans to interpret.
Text-based CAPTCHA patterns
Techniques for creating text-based CAPTCHAs include:
Gimpy—chooses an arbitrary number of words from an 850-word dictionary and provides those words in a distorted fashion.
EZ-Gimpy—is a variation of Gimpy that uses only one word.
Gimpy-r—selects random letters, then distorts and adds background noise to characters.
Simard’s HIP—selects random letters and numbers, then distorts characters with arcs and colors.
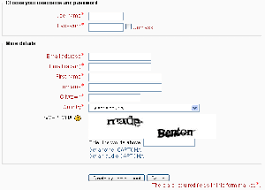
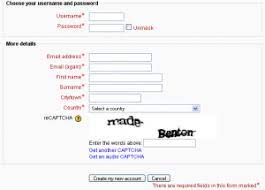
CAPTCHA Image
Image-based CAPTCHAs were developed to replace text-based ones. These CAPTCHAs use recognizable graphical elements, such as photos of animals, shapes, or scenes. Typically, image-based CAPTCHAs require users to select images matching a theme or to identify images that don’t fit.
You can see an example of this type of CAPTCHA below. Note that it defines the theme using an image instead of text.
Example of image-based CAPTCHA
Image-based CAPTCHAs are typically easier for humans to interpret than text-based. However, these tools present distinct accessibility issues for visually impaired users. For bots, image-based CAPTCHAs are more difficult than text to interpret because these tools require both image recognition and semantic classification.
Audio CAPTCHA
Audio CAPTCHAs were developed as an alternative that grants accessibility to visually impaired users. These CAPTCHAs are often used in combination with text or image-based CAPTCHAs. Audio CAPTCHAs present an audio recording of a series of letters or numbers which a user then enters.
These CAPTCHAs rely on bots not being able to distinguish relevant characters from background noise. Like text-based CAPTCHAs, these tools can be difficult for humans to interpret as well as for bots.
Math or Word Problems
Some CAPTCHA mechanisms ask users to solve a simple mathematical problem such as “3+4” or “18-3”. The assumption is that a bot will find it difficult to identify the question and devise a response. Another variant is a word problem, asking the user to type the missing word in a sentence, or complete a sequence of several related terms. These types of problems are accessible to vision impaired users, but at the same time they may be easier for bad bots to solve.
Social Media Sign In
A popular alternative to CAPTCHA is requiring users to sign in using a social profile such as Facebook, Google or LinkedIn. The user’s details will be automatically filled in using single sign on (SSO) functionality provided by the social media website.
This is still disruptive, but may actually be easier for the user to complete than other forms of CAPTCHA. An additional benefit is that it is a convenient registration mechanism.
No CAPTCHA ReCAPTCHA
This type of CAPTCHA, known for its use by Google, is much easier for users than most other types. It provides a checkbox saying “I am not a robot” which users need to select – and that’s all. It works by tracking user movements and identifying if the click and other user activity on the page resembles human activity or a bot. If the test fails, reCAPTCHA provides a traditional image selection CAPTCHA, but in most cases the checkbox test suffices to validate the user.
Imperva Bot Detection: CAPTCHA as a Last Line of Defense
Imperva provides a bot detection solution that is built for minimal business disruption. It offers several types of challenges which filter out bad bot traffic with minimal impact on human users—including device fingerprinting, cookie challenges and JavaScript challenges.
Imperva provides the option to deploy CAPTCHAs, but uses it as the final line of defense, if all other bot identification mechanisms fail. This means it will be used for a very small percentage of user traffic. Imperva does provide the option to manually enforce CAPTCHA, for websites that need a stricter approach to advanced bot protection.
In addition to providing bad bot mitigation, Imperva provides multi-layered protection to make sure websites and applications are available, easily accessible and safe. The Imperva application security solution includes:
DDoS Protection—maintain uptime in all situations. Prevent any type of DDoS attack, of any size, from preventing access to your website and network infrastructure.
CDN—enhance website performance and reduce bandwidth costs with a CDN designed for developers. Cache static resources at the edge while accelerating APIs and dynamic websites.
Cloud WAF—permit legitimate traffic and prevent bad traffic. Safeguard your applications at the edge with an enterprise‑class cloud WAF.
Gateway WAF—keep applications and APIs inside your network safe with Imperva Gateway WAF.
RASP—keep your applications safe from within against known and zero‑day attacks. Fast and accurate protection with no signature or learning mode.
What is CAPTCHA? – Google Workspace Admin Help
Send feedback help content & informationGeneral Help Center experience CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is a type of security measure known as challenge-response authentication. CAPTCHA helps protect you from spam and password decryption by asking you to complete a simple test that proves you are human and not a computer trying to break into a password protected account.
A CAPTCHA test is made up of two simple parts: a randomly generated sequence of letters and/or numbers that appear as a distorted image, and a text box. To pass a the test and prove your human identity, simply type the characters you see in the image into the text box.
Why does Google use CAPTCHA?
Google is committed to keeping your information safe and secure. CAPTCHA offers protection from remote digital entry by making sure only a human being with the right password can access your account. CAPTCHA works because computers can create a distorted image and process a response, but they can’t read or solve the problem the way a human must to pass the test.
Many web services, including Google, use CAPTCHA to help prevent unauthorized account entry. You may also see CAPTCHA on other sites that provide access to sensitive information, such as bank or credit card accounts.
When does Google use CAPTCHA?
Google uses CAPTCHA to strengthen the security around the most sensitive account access points. You may see a CAPTCHA when you:
Sign up for a new Google service (Gmail, Blogger, YouTube)
Sign up for any edition of a Google Workspace Account
Change a password on an existing account
Setup Google services for a third party device or application (such as iPhone, Outlook, ActiveSync, etc. )
I am having difficulty viewing a CAPTCHA image. What can I do?
If you can’t see a CAPTCHA image or are having trouble reading the text, refresh your browser for a new image.
Although CAPTCHAs normally rely on images, audio versions are available for the visually impaired. To access an audio version, click the link that appears near the text box as the International Symbol of Access image (the wheel-chair icon). The alternate text for this image is, “Listen and then type the numbers you hear. ” CAPTCHA is not supported for the deaf-blind community.
Was this helpful? How can we improve it?
6 reasons why your website needs a captcha form [updated …
[Updated for 2021]It’s thought that as many as 200 million captcha tests are completed online every day. If you’ve not got a captcha test on your own website, here’s everything you need to know about them and how they can benefit your business or blog. What is a captcha form? The word captcha is actually an acronym that stands for ‘completely automated public Turing test to tell computers and humans apart’. Quite a mouthful isn’t it? What this means, in a nutshell, is that a captcha test is a tool that helps to distinguish a human user from a computer user ptcha tests are often added to websites to stop them from receiving spam through the likes of contact forms. What do captcha forms look like? The original form of captcha tests, invented in the late 1990s, took the form of a panel of obscured letters or numbers. The letters were obscured by blurring, stretching or warping. It would then be the internet user’s task to identify these letters and type them into a separate area of the form. If they interpreted the letters correctly, they passed the test. Since the nineties, other forms of captcha tests have emerged. Sometimes, users will be shown an image with a grid over the top. They’ll then be asked to identify all areas of that grid that contain a certain feature – such as a street sign or a part of a parked car.
Users can also be asked to pick out specific words from a piece of text. This text is usually presented as a scanned page from a book or other publication. Some captchas are presented as simple sums, such as 4+1, as well. Plus, audio captchas exist for people with vision impairments. Most recently, Google started offering a captcha service called reCAPTCHA. The tech behind this test is a little bit more inquisitive than the that behind the original captchas. reCAPTCHA recognises that people can sometimes feel like they’re wasting their time filling in a captcha form. So, when a user arrives at a web page reCAPTCHA analyses the behaviour of that user to see how human-like it is. If the reCAPTCHA service deems the behaviour to be pretty life-like, it won’t serve up a complete captcha test. It will only ask the user to tick a box to confirm ‘I am not a robot’. If there’s anything robotic about the way the user interacts with a page, however, they’ll be asked to solve a more complicated captcha test. How do captcha tests work? At present, computer programmes lack the sophistication that humans have when it comes to processing visual data. Human minds are hard-wired to pick up on patterns in everything they see. People often see patterns where they are none – such as a face in the moon or the outline of Elvis on a burnt bit of toast. This phenomenon is called pareidolia. Computers, meanwhile, can be programmed to recognise letters and numbers. However, they stop recognising them when they are obscured or distorted too much. What are the benefits of a captcha form? Essentially captchas deter hackers from abusing online services because they block robot software from submitting fake or nefarious online requests. Captcha tests can be used to…Protect the integrity of online polls by stopping hackers using robots to send in repeated false brute force attacks on online accounts in which hackers repeatedly try to log-in using hundreds of different passwords. Prevent hackers from signing up for multiple email accounts that they’ll then go on to use for nefarious cyber criminals spamming blogs or news content pages with dodgy comments and links to other event ticket touts from using robots to bulk buy tickets for shows and make online shopping more secure. How have organisations suffered as a result of not having a captcha form? There are a few case studies of organisations and businesses who have suffered as a result of not having captcha forms on their websites.
One of the earliest cases dates back to the late nineties when social news website Slashdot published a poll asking visitors to vote for the best computer science graduate course in the USA. Students from two universities – Carnegie Mellon and MIT – used automated programs to vote repeatedly for their respective schools, and the poll became skewed and damagingly, in 2013 big supermarket brand Target suffered from a data breach that affected 70 million people. Commenting on the breach, Rocket Digital reported: “When Target hired a security company to investigate, one of the leading theories was that the breach was caused by malicious email – specifically a phishing email that went after their customer base. “They had a vendor portal that did not have a captcha or any kind of human verification in place, so a bot was able to get into the system and start transmitting data back to people who weren’t supposed to have iticisms of captcha forms [new content]A number of criticisms have been levelled at captcha forms over the years. The first criticism is that captcha forms detract from the user experience on a website. They’ve been called annoying and, in some cases, users may decide they are so frustrating that they’d rather leave the site they’re on entirely, rather than complete the captcha. The second big criticism of captcha forms is that they’re not very accessible. The lion’s share of captcha forms require the user to be able to see. Audio alternatives to captchas are available but one study by the National Federation for the Blind found that blind people were only able to complete these audio captchas 46 per cent of the time. More recently, Google’s reCAPTCHA technology has been attacked for consuming too much data. In April 2020 big security brand Cloudflare announced that it would be moving from using Google’s reCAPTCHA to using hCaptcha saying: “hCaptcha don’t sell personal data; they collect only minimum necessary personal data and they are transparent in describing the info they collect and how they use and/or disclose it. ” On top of this, cyber criminals are starting to use captcha forms themselves. Digital technology magazine Ars Technica recently reported: “Microsoft recently spotted an attack group distributing a malicious Excel document on a site requiring users to complete a CAPTCHA, most likely in an attempt to thwart automated detection by good guys. ” How do I add a captcha form to my website? If your website is based on WordPress, you can add a captcha plugin to your site. There are lots of options in the WordPress plugin directory, but you’ll want to choose one that has been updated recently and has a decent amount of active installations – like reCaptcha by BestWebSoft. For other websites, you might need a little bit of tech experience, in the form of HTML knowledge, to add a captcha to your website. If your business has its own web development team then they can do it easily and quickly in-house, or you can contact your web designer to complete the task for you. Google offers developers detailed instructions on how to install a reCAPTCHA, for free, on its help pages. hCaptcha also features a developer guide on its future of captcha? [new content]As bots become more sophisticated, captchas will need to keep up. Industry commentators suggest that an element of gamification may need to be added to captchas of the future – although this doesn’t solve the accessibility issue. Other experts suggest that captchas may eventually be replaced altogether with biometric checks – such as quick eye scans. Need more protection for your website? Check out our Sucuri website security product. With prices starting at just £4. 99 a month, it polices websites for malware and purges any it detects. Find out more on our Security Pages.
Frequently Asked Questions about why captcha code is used
What does CAPTCHA code mean?
CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is a type of security measure known as challenge-response authentication. … A CAPTCHA test is made up of two simple parts: a randomly generated sequence of letters and/or numbers that appear as a distorted image, and a text box.
What are the advantages of CAPTCHA?
What are the benefits of a captcha form? Essentially captchas deter hackers from abusing online services because they block robot software from submitting fake or nefarious online requests. Protect the integrity of online polls by stopping hackers using robots to send in repeated false responses.Jan 28, 2021