What Is User Agent
User-Agent – HTTP – MDN Web Docs
SyntaxUser-Agent:
Common format for web browsers:
User-Agent: Mozilla/5. 0 (
Directives
Zero or more comments containing more details. For example, sub-product information.
Firefox UA stringFor more on Firefox- and Gecko-based user agent strings, see the Firefox user agent string reference. The UA string of Firefox is broken down into 4 components:
Mozilla/5. 0 (platform; rv:geckoversion) Gecko/geckotrail Firefox/firefoxversion
Mozilla/5. 0 is the general token that says that the browser is Mozilla-compatible. For historical reasons, almost every browser today sends it.
platform describes the native platform that the browser is running on (Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, etc. ) and if it is a mobile phone. Firefox OS phones say Mobile — the web is the platform. Note that platform can consist of multiple “;”-separated tokens. See below for further details and examples.
rv:geckoversion indicates the release version of Gecko (such as “17. 0”). In recent browsers, geckoversion is the same as firefoxversion.
Gecko/geckotrail indicates that the browser is based on Gecko. (On the desktop, geckotrail is always the fixed string 20100101. )
Firefox/firefoxversion indicates that the browser is Firefox and provides the version (such as “17. 0”).
ExamplesMozilla/5. 0 (Windows NT 6. 1; Win64; x64; rv:47. 0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/47. 0
Mozilla/5. 0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X x. y; rv:42. 0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/42. 0
Chrome UA stringThe Chrome (or Chromium/Blink-based engines) user agent string is similar to Firefox’s. For compatibility, it adds strings like KHTML, like Gecko and Safari. ExamplesMozilla/5. 0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537. 36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51. 0. 2704. 103 Safari/537. 36
Opera UA stringThe Opera browser is also based on the Blink engine, which is why it almost looks the same as the Chrome UA string, but adds “OPR/
Older, Presto-based Opera releases used:
Opera/9. 80 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X; U; en) Presto/2. 2. 15 Version/10. 00
Opera/9. 60 (Windows NT 6. 0; U; en) Presto/2. 1. 1
Microsoft Edge UA stringThe Edge browser is also based on the Blink engine. It adds “Edg/
Safari UA stringIn this example, the user agent string is mobile Safari’s version. It contains the word “Mobile”. 0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 13_5_1 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605. 15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/13. 1 Mobile/15E148 Safari/604. 1
Internet Explorer UA stringExamplesMozilla/5. 0 (compatible; MSIE 9. 0; Windows Phone OS 7. 5; Trident/5. 0; IEMobile/9. 0)
Crawler and bot UA stringsExamplesMozilla/5. 0 (compatible; Googlebot/2. 1; +)
Mozilla/5. 0 (compatible; YandexAccessibilityBot/3. 0; +)
Examplescurl/7. 64. 1
PostmanRuntime/7. 26. 5
SpecificationsSpecificationHypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1. 1): Semantics and Content (HTTP/1. 1)# compatibilityBCD tables only load in the browserSee also
User-Agent detection, history and checklist
Firefox user agent string reference
Browser detection using the user agent
User Agent – Definition, Types, and Importance – Seobility Wiki
Contents
1 Definition
2 Transmitting the user agent through the HTTP header
3 Types of user agents
4 Importance of user agents
5 Related links
6 Similar articles
Definition
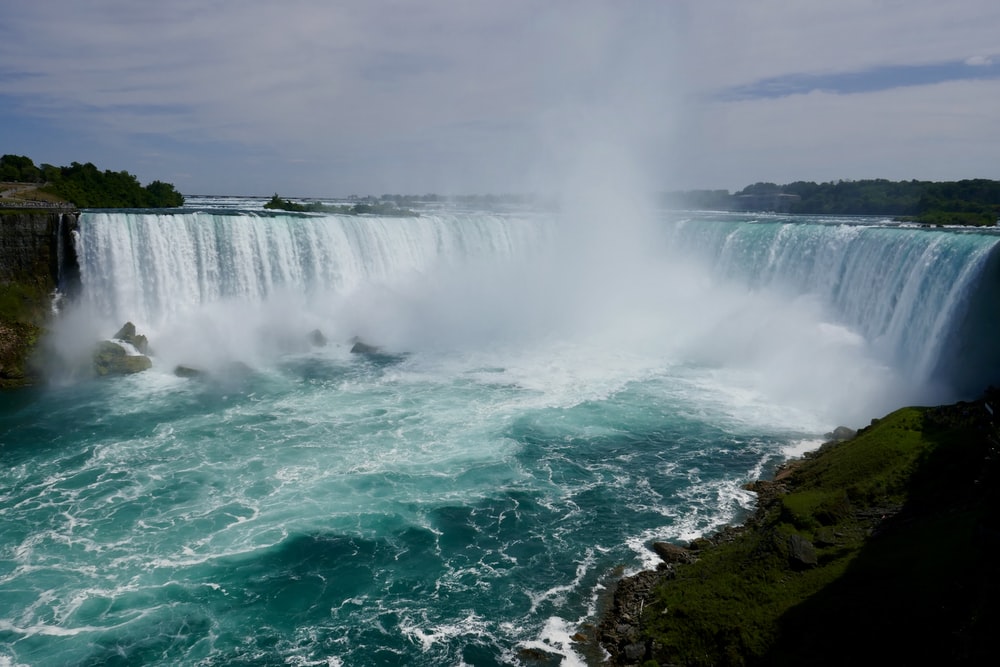
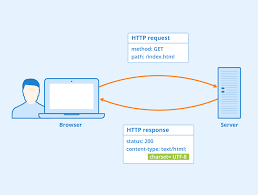
A user agent (short: UA) is software that communicates with servers in a network. An example would be a web browser that retrieves a web page from a server on the internet and displays it. The user agent acts as a mediator between the user and the web server just like a human agent. It processes the user’s instructions, transfers them and receives the requested data. The user agent transmits information such as the browser version, installed plugins, and other data to the web server. Based on this data, the server can assess the capabilities of the user agent and deliver the appropriate data to it.
Figure: User Agent – Author: Seobility – License: CC BY-SA 4. 0
The information that identifies the user agent is transferred to the web server in the HTTP request header. Each header contains a characteristic string that servers can use to identify the application type, operating system, software vendor, or software version of the requesting user agent.
The structure and content of this information are not standardized. Each developer can insert and submit his own information. For example, the basic syntax for a Firefox web browser is:
Mozilla/5. 0 (platform; rv:geckoversion) Gecko/geckotrail Firefox/firefoxversion
Mozilla/5. 0 is a general token stating the web browser is compatible with Mozilla. Modern browsers use this token for historical reasons only, since it is no longer of great importance.
platform describes the native platform the web browser operates on – for example, Windows, Mac, Linux or Android and whether it is a mobile phone or not. Firefox OS for mobile simply puts the word “Mobile” here.
rv:geckoversion indicates the version of Gecko. Gecko is an HTML rendering engine that web browsers use to display a web page. In current browsers, geckoversion is the same as firefoxversion.
Gecko/geckotrail indicates that the browser is based on Gecko. On desktop, geckotrail has the fixed string “20100101”.
Firefox/firefoxversion indicates the browser is a Firefox version with the specified version number.
An example of a Firefox browser on a desktop operating on Windows would look like this:
Mozilla/5. 0 (Windows NT 6. 1; Win64; x64; rv:64. 0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/64. 0
Information provided by the agent can be modified or falsified. One example would be some mobile web browsers, which can switch between mobile or desktop mode to get access to websites that only allow desktop computers.
In the early days of the internet, Microsoft’s first Internet Explorer pretended to be a Netscape browser to access web pages designed for Netscape Navigator, the dominant browser on the market back then.
Types of user agents
Browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google’s Chrome as well as Safari and Opera are examples of user agents. However, other applications can also act as user agents. Examples are:
Crawlers: Googlebot, Yahoo! Slurp, MSN bot
Game consoles: PlayStation, Wii, PlayStation Portable and Bunjalloo (the browser on the Nintendo DS)
Legacy operating systems: AmigaVoyager
Link checkers: e. g. W3C-Checklink
SEO tools / on-page crawlers: e. SeobilityBot
Web applications: Flash Player, Adobe Acrobat Reader, feed readers, screen readers, validators, media players, streaming portals
Not all user agents are controlled or instructed by humans. Search engine crawlers are an example of user agents that visit websites automatically.
Importance of user agents
Once a user agent has identified itself to the web server, a process called content negotiation begins. Content negotiation is a mechanism defined in HTTP that allows you to provide different versions of a document or another resource using the same URL. Browsers can specify which version best suits their capabilities with the help of user agent information and request the fitting resource for their needs. A classic application of this mechanism is providing an image in GIF as well as PNG format, and delivering the GIF version to user agents that cannot display PNG images (such as older versions of MS Internet Explorer). Similarly, different stylesheets (CSS), JavaScript, or the mobile version of a web page can be rendered based on browser capabilities. If the user agent transmits the language setting, the appropriate language version of a document can be delivered. A PDF reader can access PDF documents and a media player can access videos.
When an application receives content tailored to its user agent, this process is referred to as agent name delivery. Search engine optimization uses this process to present different content to search engine bots compared to real visitors’ user agents. When this black hat SEO tactic referred to as cloaking is used, visitors see a web page optimized for humans whereas crawlers access content and structure that is mostly simple and optimized for high rankings in search results. However, search engines know this spam technique and therefore often act as browsers.
Similar articles
Proxy Server
Black Hat SEO
Dedicated Server
Definition of User Agent – WAI UA Wiki – W3C
Definition: A user agent is any software that retrieves, renders and facilitates
end user interaction with Web content, or whose user interface is
implemented using Web technologies. {revised from)
Introduction in Guidelines
revisions and additions to A user agent is any software that retrieves and presents Web content for end users or is implemented using Web technologies. User agents include Web browsers, media players, and plug-ins that help in retrieving, rendering and interacting with Web content. The family of user agents also includes operating system shells, consumer electronics with Web-widgets, and stand-alone applications or embedded applications whose user interface is implemented as a combination of Web technologies.
comment: greg – I suggest having at least a user-friendly paragraph in the intro that explicitly refers readers to the glossary for a formal, normative definition.
While rendering engines and other technologies used to build user agents are not by themselves considered user agents, it is fundamental to user agent accessibility that these technologies support user agent requirements. In building a user agent the developer should fully understand the support for UAAG 2. 0 when selecting technologies.
What qualifies as a User Agent?
The following tests can be used to determine if software qualifies as a user agent for the purposes of these guidelines. It divides potential user agents into Primary Agents (the traditional “browser”), Extensions and Plug-ins, and Web-based User Agents.
If the following three conditions are met then it is a Primary User Agent and Must Conform to UAAG:
If it is a standalone application; and
If it interprets any w3c specified language; and
If it provides a user interface or interprets either a procedural or declarative language that may be used to provide a user interface.
If the following two conditions are met then it is a User Agent Extension or Plug-In and Must Conform to UAAG:
If it is launched by, or extends the functionality of, a Primary User Agent; and
If post-launch user interaction either becomes part of, or is within the bounds of, the Primary User Agent.
If the following three conditions are met then it is a Web-Based User Agent and Must Conform to UAAG:
If the user interface is generated by the interpretation of either a procedural or declarative language; and
If this interpretation is by a Primary User Agent, User Agent Extension or Plug-In; and
If user interaction is not passed to and from the Primary User Agent, User Agent Extension or Plug-In, or if user interaction does not modify the Document Object Model of its containing document.
Frequently Asked Questions about what is user agent
What is an example of a user agent?
Browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google’s Chrome as well as Safari and Opera are examples of user agents. However, other applications can also act as user agents. Examples are: Crawlers: Googlebot, Yahoo!
What’s in a user agent?
A user agent is any software that retrieves and presents Web content for end users or is implemented using Web technologies. User agents include Web browsers, media players, and plug-ins that help in retrieving, rendering and interacting with Web content.
What is device user agent?
The User-Agent tells the server what the visiting device is (among many other things) and this information can be used to determine what content to return. … Of course this requires using a device detection solution which translates UAs into understandable software and hardware information.Oct 23, 2018


