What Is A Proxy Website
What is a Proxy Server and How Does it Work? – Varonis
The actual nuts and bolts of how the internet works are not something people often stop to consider. The problem with that is the inherent danger of data security breaches and identity theft that come along with the cute dog pictures, 24-hour news updates, and great deals online.
But what actually happens when you browse the web? You might be using a proxy server at your office, on a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or you could be one of the more tech-savvy who always use a proxy server of some kind or another.
Discover the Top 5 Remote Security Threats to your workforce with our Free Whitepaper
“It’s a new world of remote work and this was a jumpstart on securing it. ”
What’s a Proxy Server?
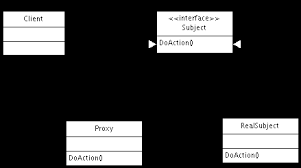
A proxy server is any machine that translates traffic between networks or protocols. It’s an intermediary server separating end-user clients from the destinations that they browse. Proxy servers provide varying levels of functionality, security, and privacy depending on your use case, needs, or company policy.
If you’re using a proxy server, traffic flows through the proxy server on its way to the address you requested. The request then comes back through that same proxy server (there are exceptions to this rule), and then the proxy server forwards the data received from the website to you.
If that’s all it does, why bother with a proxy server? Why not just go straight from to the website and back?
Modern proxy servers do much more than forward web requests, all in the name of data security and network performance. Proxy servers act as a firewall and web filter, provide shared network connections, and cache data to speed up common requests. A good proxy server keeps users and the internal network protected from the bad stuff that lives out in the wild internet. Lastly, proxy servers can provide a high level of privacy.
How Does a Proxy Server Operate?
Every computer on the internet needs to have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) Address. Think of this IP address as your computer’s street address. Just as the post office knows to deliver your mail to your street address, the internet knows how to send the correct data to the correct computer by the IP address.
A proxy server is basically a computer on the internet with its own IP address that your computer knows. When you send a web request, your request goes to the proxy server first. The proxy server then makes your web request on your behalf, collects the response from the web server, and forwards you the web page data so you can see the page in your browser.
When the proxy server forwards your web requests, it can make changes to the data you send and still get you the information that you expect to see. A proxy server can change your IP address, so the web server doesn’t know exactly where you are in the world. It can encrypt your data, so your data is unreadable in transit. And lastly, a proxy server can block access to certain web pages, based on IP address.
What are Forward Proxies
A forward proxy server sits between the client and an external network. It evaluates the outbound requests and takes action on them before relaying that request to the external resource.
Most proxy services that you’re likely to encounter are forward proxies. Virtual Private Networks and Web content filters are both examples of forward proxies.
What are Reverse Proxies
A reverse proxy server sits between a network and multiple other internal resources. A large website might have dozens of servers that collectively serve requests from a single domain. To accomplish that, client requests would resolve to a machine that would act as a load balancer. The load balancer would then proxy that traffic back to the individual servers.
Some popular open source reverse proxies are:
Varnish
Squid
Why Should You Use a Proxy Server?
There are several reasons organizations and individuals use a proxy server.
To control internet usage of employees and children: Organizations and parents set up proxy servers to control and monitor how their employees or kids use the internet. Most organizations don’t want you looking at specific websites on company time, and they can configure the proxy server to deny access to specific sites, instead redirecting you with a nice note asking you to refrain from looking at said sites on the company network. They can also monitor and log all web requests, so even though they might not block the site, they know how much time you spend cyberloafing.
Bandwidth savings and improved speeds: Organizations can also get better overall network performance with a good proxy server. Proxy servers can cache (save a copy of the website locally) popular websites – so when you ask for, the proxy server will check to see if it has the most recent copy of the site, and then send you the saved copy. What this means is that when hundreds of people hit at the same time from the same proxy server, the proxy server only sends one request to This saves bandwidth for the company and improves the network performance.
Privacy benefits: Individuals and organizations alike use proxy servers to browse the internet more privately. Some proxy servers will change the IP address and other identifying information the web request contains. This means the destination server doesn’t know who actually made the original request, which helps keeps your personal information and browsing habits more private.
Improved security: Proxy servers provide security benefits on top of the privacy benefits. You can configure your proxy server to encrypt your web requests to keep prying eyes from reading your transactions. You can also prevent known malware sites from any access through the proxy server. Additionally, organizations can couple their proxy server with a Virtual Private Network (VPN), so remote users always access the internet through the company proxy. A VPN is a direct connection to the company network that companies provide to external or remote users. By using a VPN, the company can control and verify that their users have access to the resources (email, internal data) they need, while also providing a secure connection for the user to protect the company data.
Get access to blocked resources: Proxy servers allow users to circumvent content restrictions imposed by companies or governments. Is the local sportsball team’s game blacked out online? Log into a proxy server on the other side of the country and watch from there. The proxy server makes it look like you are in California, but you actually live in North Carolina. Several governments around the world closely monitor and restrict access to the internet, and proxy servers offer their citizens access to an uncensored internet.
Now that you have an idea about why organizations and individuals use a proxy server, take a look at the risks below.
Proxy Server Risks
You do need to be cautious when you choose a proxy server: a few common risks can negate any of the potential benefits:
Free proxy server risks
You know the old saying “you get what you pay for? ” Well, using one of the many free proxy server services can be quite risky, even the services using ad-based revenue models.
Free usually means they aren’t investing heavily in backend hardware or encryption. You’ll likely see performance issues and potential data security issues. If you ever find a completely “free” proxy server, tread very carefully. Some of those are just looking to steal your credit card numbers.
Browsing history log
The proxy server has your original IP address and web request information possibly unencrypted, saved locally. Make sure to check if your proxy server logs and saves that data – and what kind of retention or law enforcement cooperation policies they follow.
If you expect to use a proxy server for privacy, but the vendor is just logging and selling your data you might not be receiving the expected value for the service.
No encryption
If you use a proxy server without encryption, you might as well not use a proxy server. No encryption means you are sending your requests as plain text. Anyone who is listening will be able to pull usernames and passwords and account information really easily. Make sure whatever proxy server you use provides full encryption capability.
Types of Proxy Servers
Not all proxy servers work the same way. It’s important to understand exactly what functionality you’re getting from the proxy server, and ensure that the proxy server meets your use case.
Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy tells websites that it is a proxy server and it will still pass along your IP address, identifying you to the web server. Businesses, public libraries, and schools often use transparent proxies for content filtering: they’re easy to set up both client and server side.
Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy will identify itself as a proxy, but it won’t pass your IP address to the website – this helps prevent identity theft and keep your browsing habits private. They can also prevent a website from serving you targeted marketing content based on your location. For example, if knows you live in Raleigh, NC, they will show you news stories they feel are relevant to Raleigh, NC. Browsing anonymously will prevent a website from using some ad targeting techniques, but is not a 100% guarantee.
Distorting proxy
A distorting proxy server passes along a false IP address for you while identifying itself as a proxy. This serves similar purposes as the anonymous proxy, but by passing a false IP address, you can appear to be from a different location to get around content restrictions.
High Anonymity proxy
High Anonymity proxy servers periodically change the IP address they present to the web server, making it very difficult to keep track of what traffic belongs to who. High anonymity proxies, like the TOR Network, is the most private and secure way to read the internet.
Proxy servers are a hot item in the news these days with the controversies around Net Neutrality and censorship. By removing net neutrality protections in the United States, Internet Service Providers (ISP) are now able to control your bandwidth and internet traffic. ISPs can potentially tell you what sites you can and cannot see. While there’s a great amount of uncertainty around what is going to happen with Net Neutrality, it’s possible that proxy servers will provide some ability to work around an ISPs restrictions.
Varonis analyzes data from proxy servers to protect you from data breaches and cyber attacks. The addition of proxy data gives more context to better analyze user behavior trends for abnormalities. You can get an alert on that suspicious activity with actionable intelligence to investigate and deal with the incident.
For example, a user accessing GDPR data might not be significant on its own. But if they access GDPR data and then try to upload it to an external website, it could be an exfiltration attempt and potential data breach. Without the context provided by file system monitoring, proxy monitoring, and Varonis threat models, you might see these events in a vacuum and not realize you need to prevent a data breach.
Get a 1:1 demo to see these threat models in action – and see what your proxy data could be telling you.
What Is a Proxy Server and How Do Proxies Work? – DZone
You might have already heard about proxies and proxy servers. But if you aren’t entirely familiar with them, this article will help you catch up with this web technology and see all the benefits of using proxy servers.
What Are Proxies?
A web proxy is some kind of intermediate between a web user and an online resource. When visiting a website directly, you send a web request containing information about yourself (the server or PC that you are using, your location, browser fingerprints, IP address, etc. ). As a response to this data sent, the web resource provides you with the content you requested.
Unlike a direct connection between users and websites, a proxy-based connection provides a gateway for your web request and the data you will receive back from the website. Proxies can hide or modify your web request data and filter the website content preventing you from getting unwanted information. This also ensures anonymous web browsing and data collection from your end.
You may also like:
Linux Proxy Server
Usually, proxies are divided into two types: shared and dedicated proxies.
Shared Proxy
A shared proxy is a public proxy that can be easily accessed by anyone. As a rule, you can get shared proxies for free, without any restrictions on the number of users they serve. Such servers often get overloaded by hundreds of web users. This slows down the Internet connection and often results in huge lags and even crashes.
By using shared proxies, you will have to wait minutes for a web page to load, making it virtually impossible for you to surf the web. Moreover, browsing the Internet via these open proxies is pretty much risky, since they can be used by providers as a way to collect and steal your personal information.
There are also semi-dedicated proxies that have a limited number of users. They suit small groups of people, like companies or schools, in order for them to create a shared network connection.
Dedicated Proxy
A dedicated proxy allows you to use a proxy privately, which means you are the only person that uses it. This empowers you to browse completely anonymously and securely with high page load speed.
What Is a Proxy Server?
Now, you are probably wondering “what is a proxy server”? A proxy server or proxy is a server that works as an intermediate connection point between you and the web page you visit. Proxy servers process your web request and the website data, making your web browsing secure and private.
How Do Proxy Servers Work?
Each time you’re visiting a website by hitting a link or typing the web address manually in your browser, you create and submit a web request that’s forwarded to a proxy server. Then, the proxy server modifies and encrypts your data such as your IP (Internet Protocol) address and sends it to the web resource.
After that, the website sends its data back to the proxy server that processes it before transferring the web page information to you. This way, it works as a firewall or a web filter for you to get only the information you want to receive. Now that you have a glimpse of what’s behind the question “how does a proxy server work?, let’s take a closer look at which types of proxy servers exist.
Depending on the network setup and configuration involving a proxy, there can be three distinct types of proxy servers out there:
Forward Proxy Server
Forward Proxy Servers are commonly used by internal networks. How does a web proxy work when it comes to Forward Proxy Servers? Once one of the clients sends a request to get connected to a particular website, it first has to pass through a Forward Proxy Server that decides whether or not the client is allowed to approach this resource. If yes, the connection request goes to the external server that doesn’t see the client’s IP address but sees only the connection request sent from the Forward Proxy Server.
A Forward Proxy Server provides full administrative control over the local network connections. It acts as a shield or a firewall that lets the Administrators restrict access to unwanted web resources by the internal network clients. You can see this kind of proxy servers in schools and universities.
Reverse Proxy Server
Unlike a Forward Proxy Server, the Reverse Proxy Server works on the side of a website (or web service) hiding the IP addresses within the internal network from the external users. The Reverse Proxy decides whether the web users may see the content of a website or use a web service or not.
As far as the benefits are concerned, the Reverse Proxy Servers make it very hard for hackers to attack the internal servers. Besides, it functions as a load balancer in order to disperse the data between the internal servers that prevent overloading by tons of connection requests. Proxies of this type are used by web service providers.
Open Proxy Servers
Open Proxy Servers allow both forwarding the requests by internet users and receiving responses from websites. The key feature of this kind of proxy servers is hiding the user’s original IP address from the web. Unlike dedicated proxies, open proxy servers do not require authentication on the side of the user and are prone to abuse and malware infections.
Why Should You Use a Proxy Server?
Now, you have a better understanding of what a proxy server is and how to use a proxy. But what is a proxy server used for?
If you are thinking about whether or not you should opt for a proxy, there are a lot of advantages that will convince you to start using it.
More Privacy
Proxies can encrypt your data, configuring your IP address so that you can hide your real location to “outplay” the network with no effort. This way, the server you are sending your request to won’t know your actual IP address and other personal information. It allows you to avoid risks like hacking attempts and identity thefts.
Access to Any Website
Alongside more anonymous browsing, there are other benefits that come along with hiding your IP address. Imagine you want to visit a website that restricts the contents to be viewed in your country. In this case, you can change your IP address. Due to this, you can gain access to virtually any website on the web that has this kind of limitation.
Higher Security
Since you can keep your data private, your internet connection becomes more secure. You can configure and modify your proxy in order for the web to see only the info you allow it to get access to. Proxies also work as a web firewall that protects your device and filters the web resources that could probably contain malware.
Improved Performance
Proxy servers can also improve your browsing performance. For example, once you visit a website, it gets saved in the cache of your proxy server. Next time you reach for the website, the proxy sends a request to the website server to look for any changes, and if no changes are detected, it will show you the cached version of the website. This way, you can cut down the loading time of websites you’ve already visited. It is especially beneficial when it comes to companies and organizations.
Further Reading
Why Proxies Are Important for Microservices.
The Basics Of Web Scraping With Proxies.
SOCKS5 Proxy and its Benefits.
Topics:
proxy,
proxy server,
security,
reverse proxy,
data privacy

Proxy Services Are Not Safe. Try These Alternatives | WIRED
Millions of people across the world use free proxy services to bypass censorship filters, improve online security, and access websites that aren’t available in their country. But an analysis has found those free services come at an unexpected cost for users: their privacy and security. Christian Haschek, an Austria-based security researcher, wrote a script that analyzed 443 open proxies, which route web traffic through an alternate, often pseudo-anonymous, computer network. The script tested the proxies to see if they modified site content or allowed users to browse sites while using encryption. According to Haschek’s research, just 21 percent of the tested proxies weren’t “shady. “Haschek found that the other 79 percent of surveyed proxy services forbid secure, HTTPS is commonly used to encrypt Web traffic, allowing users to enter credit cards, passwords, and other sensitive information in a manner that makes it difficult for hackers and intermediaries to intercept. By preventing customers from using the Web securely, Haschek warns these open proxies “can analyze your traffic and steal your logins. “Free proxies are also manipulating websites directly. Haschek reports that 16. 6 percent of proxies change HTML and 8. 5 percent modified websites’ JavaScript. In most cases, this was done merely to inject advertising into websites. However, Haschek speculates that these services are “probably also cookie stealing. “Popularity SurgeProxy usage has been growing over the years along with the rise of content streaming services and growing fears of government surveillance of internet activity. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), which encrypts all your traffic and routes it through another server to mask your location, are commonly used by people looking to bypass geolocation restrictions on services such as Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer. And by masking user’s locations, software and media pirates have also flocked to VPNs to make it more difficult for content owners to sue them in services are also popular in countries with strict Internet laws. They have been used in China, particularly by foreigners looking to access Western websites blocked by the Great Firewall, until the Chinese government moved to block VPN access earlier this year. In April, many Australians started using VPNs after the government passed a mandatory data retention law. As a result, CNET reported that one VPN provider’s Australian business increased 500 percent between early March and the same time, in the past few months free VPN services have been tied to deceptive business practices. Hola, an Israeli VPN service that boasts over 48 million users, was widely criticized last month for selling its free-tier users’ idle bandwidth. This meant Hola’s millions of free users were unknowingly turned into a botnet that was utilized for criminal activities, including repeated denial-of-service attacks against the message board 8chan. Haschek’s analysis didn’t uncover anything quite so sinister, but noted some of the reviewed services were “definitely bad adware. ” A previous report from the security researcher noted that many of these free proxies exist because establishing the service serves as “an easy way to infect thousands of users and collect their data. “According to that report, Haschek observed that controlling a VPN services makes it is easy to manipulate websites to steal login information, banking and credit card accounts, turn users into a distributed denial-of-service attack botnet, and monitor all their Web nding Safe AlternativesTo help combat the security vulnerabilities users expose themselves to when using free proxies, Haschek released a tool called Proxy Checker, which performs a cursory evaluation on any proxy service in use to ensure it isn’t manipulating content or forcing users to forgo Haschek recommends avoiding free proxies altogether. Fortunately, secure alternatives a paid VPN or proxy service is a good place to start. Because these paid services rely on monthly subscription revenue to support their operation, they don’t have to resort to breaking encryption to serve ads or selling there users’ traffic off, as was the case with Hola. For Jonathan Roudier, president of the widely recommended VPN service Private Internet Access, privacy is the focus. “We wanted to offer the best privacy and security available, ” Roudier told WIRED. “That comes at a cost. “Roudier noted that paid VPN services have other benefits over free offerings that go beyond security, including providing customer support, not placing bandwidth restrictions on users, and allowing users to choose which encryption method to ever, not all paid VPNs services equally prioritize their users’ security. When shopping for a VPN service, it is recommended to find a service that does not log its customers’ traffic and prevents an anonymity-unmasking issue known as IPv6 leakage. Both Private Internet Access and another popular service, Mullvad, carry that level of security. Another provider, TorGuard, does not log user activity and allows users to prevent IPv6 leakage through an advanced setting in its VPN can also use Tor, which is both free and regarded as one of the most secure anonymous browsing services available. However, Tor relies on volunteer-run servers to relay traffic and bounces that traffic across the globe, which means you can kiss smoothly streaming of HD video goodbye. Ultimately, there is no silver bullet to ensure complete security and privacy online. But when entrusting your Internet traffic to third party, its best to use a service that isn’t basing its business on serving ads—and weakening your security.
Frequently Asked Questions about what is a proxy website
What are proxy websites?
What Are Proxies? A web proxy is some kind of intermediate between a web user and an online resource. When visiting a website directly, you send a web request containing information about yourself (the server or PC that you are using, your location, browser fingerprints, IP address, etc.).Feb 12, 2020
Are proxy websites safe?
Millions of people across the world use free proxy services to bypass censorship filters, improve online security, and access websites that aren’t available in their country. … But an analysis has found those free services come at an unexpected cost for users: their privacy and security.Jul 6, 2015
What are proxy sites used for?
A proxy server provides a gateway between users and the internet. It is a server, referred to as an “intermediary” because it goes between end-users and the web pages they visit online. When a computer connects to the internet, it uses an IP address.